Engine Water Pump Shapes Future Vehicle Thermal Systems
Within the internal combustion engine, a component often taken for granted plays a mission-critical role in vehicle health and performance: the engine water pump. Traditionally viewed as a simple mechanical circulator, the engine water pump has undergone significant evolution, transitioning into a more sophisticated element of advanced thermal management systems. Its core function remains indispensable, but how it achieves that function is changing, driven by demands for greater efficiency, reduced emissions, and integration with hybrid and electric vehicle architectures.
What is the Basic Function of an Engine Water Pump?
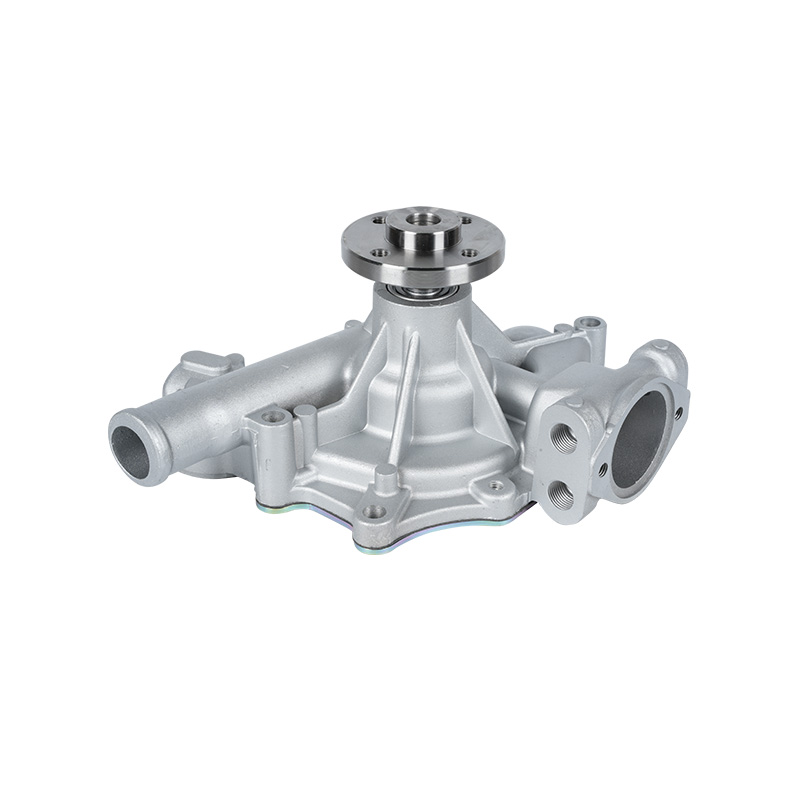
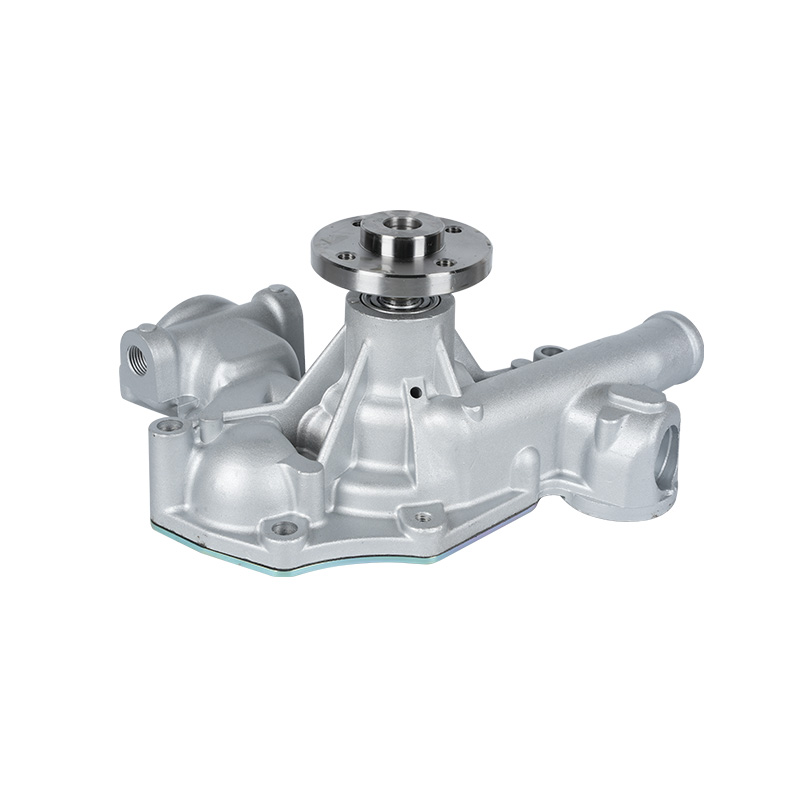
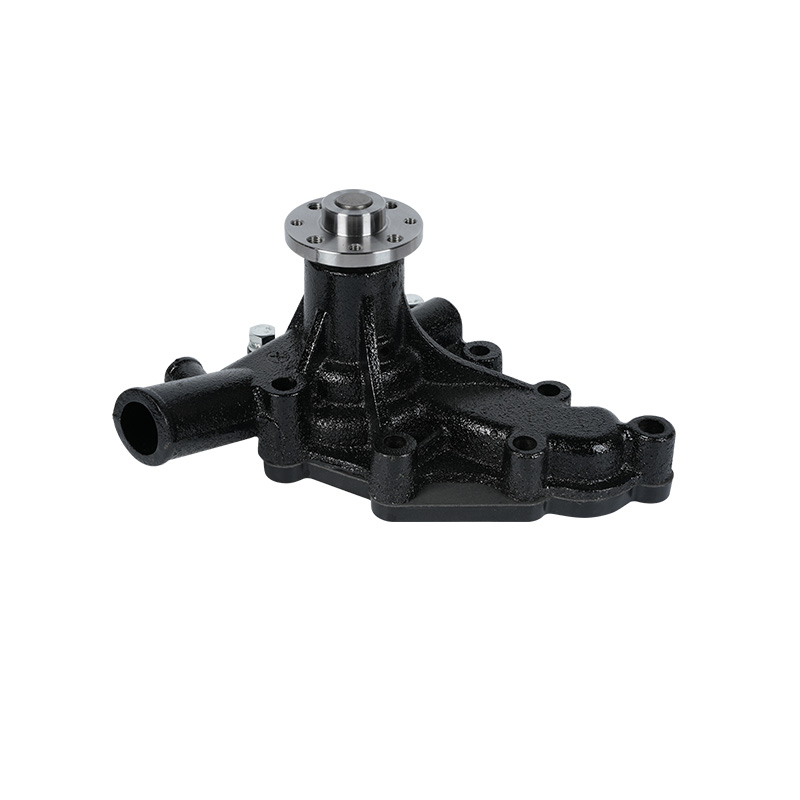
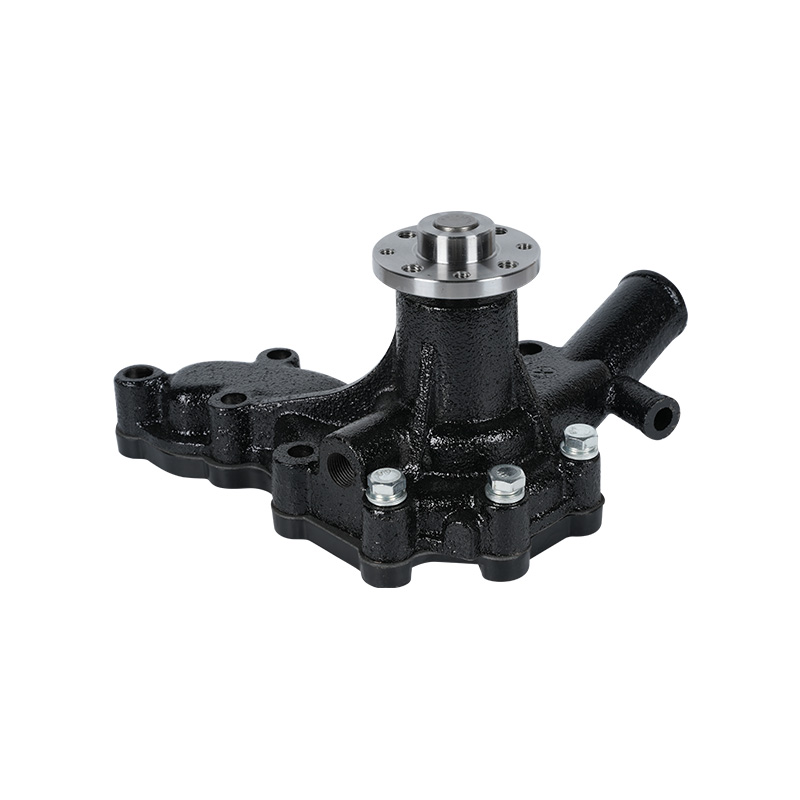
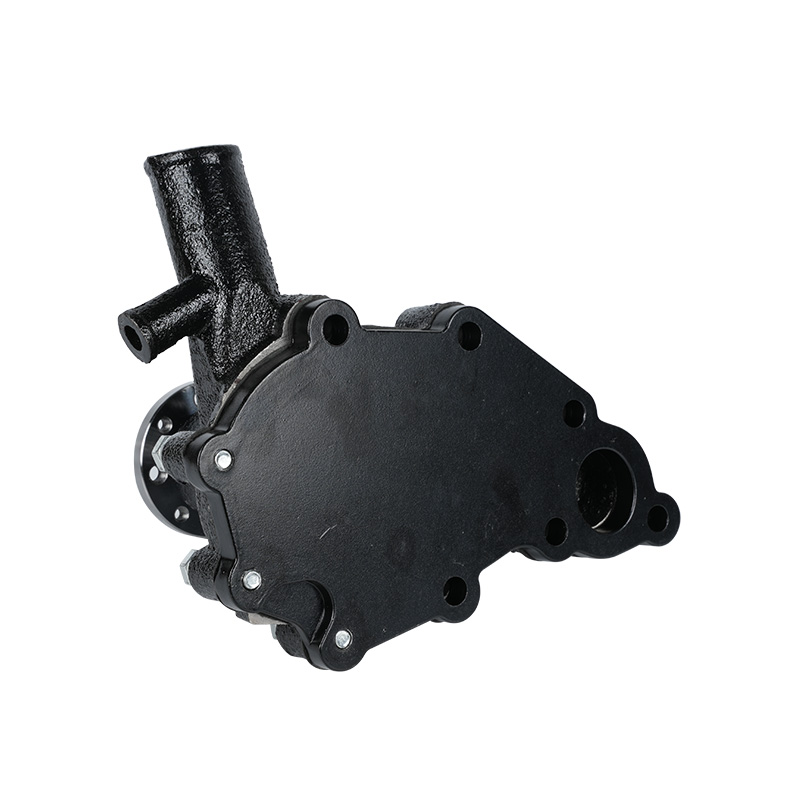
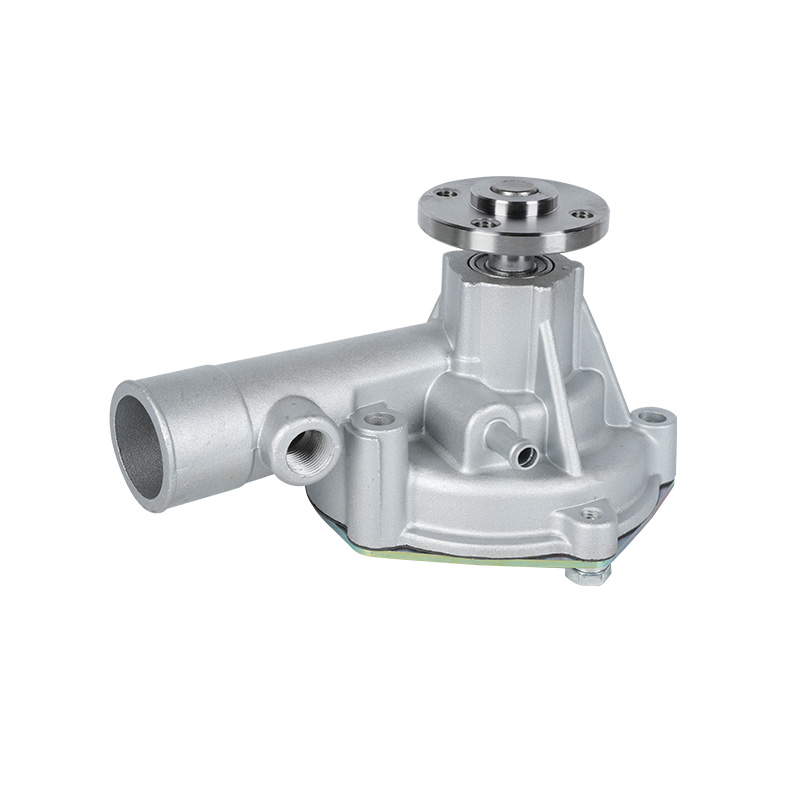
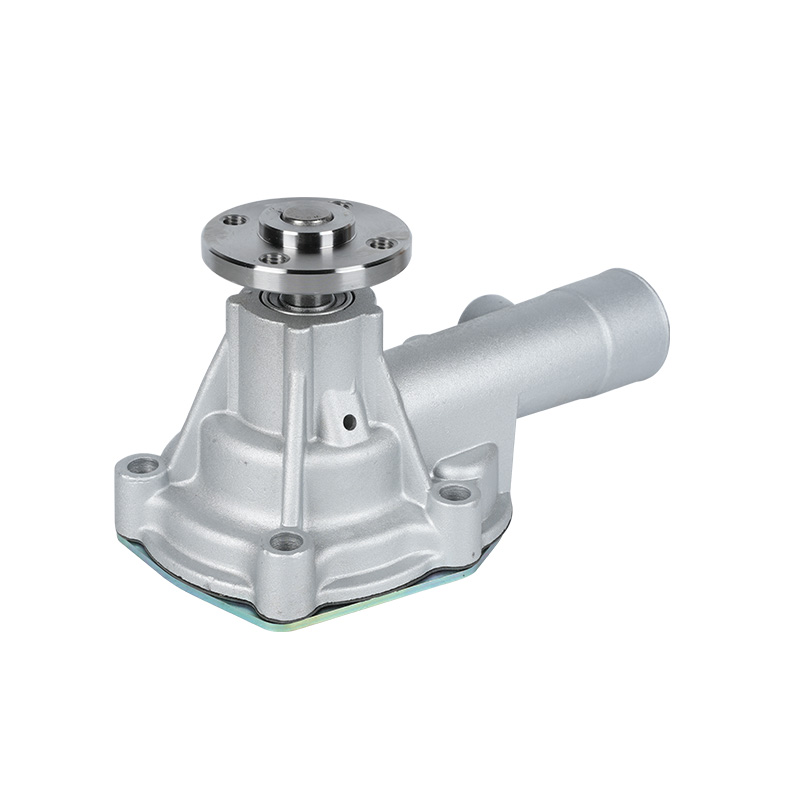
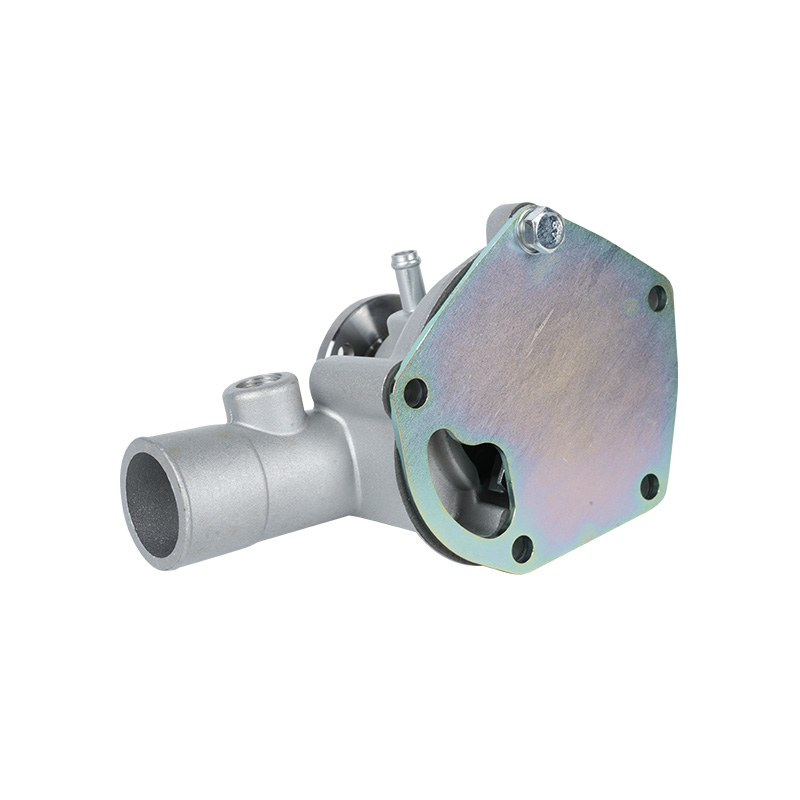
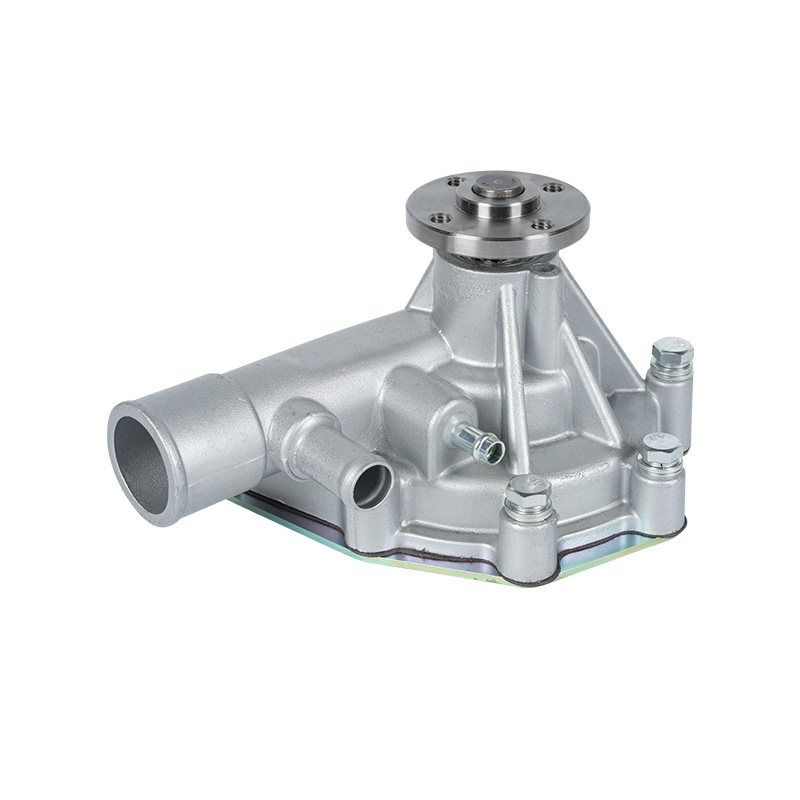
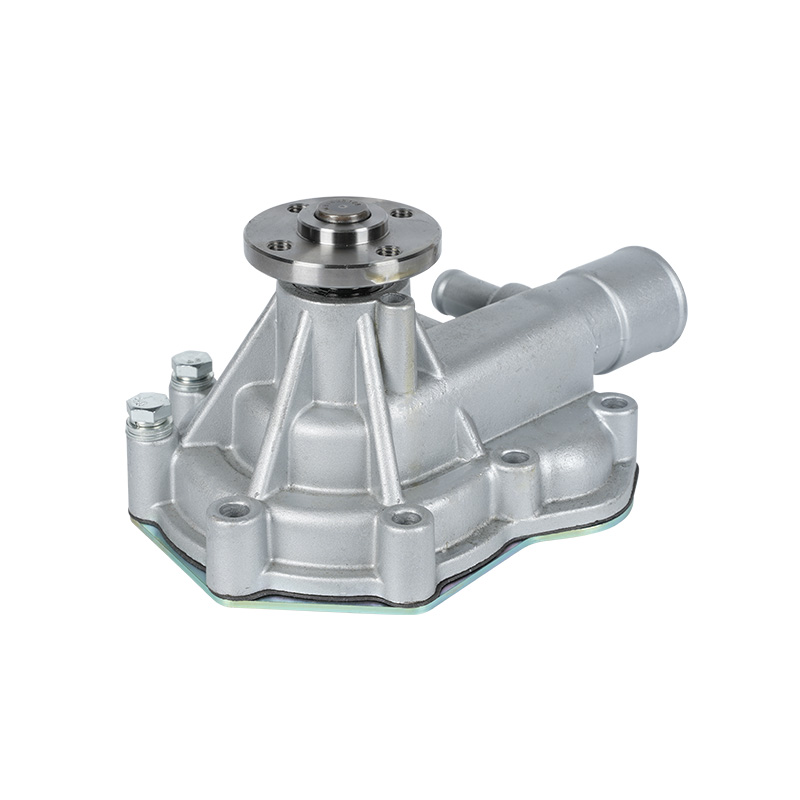
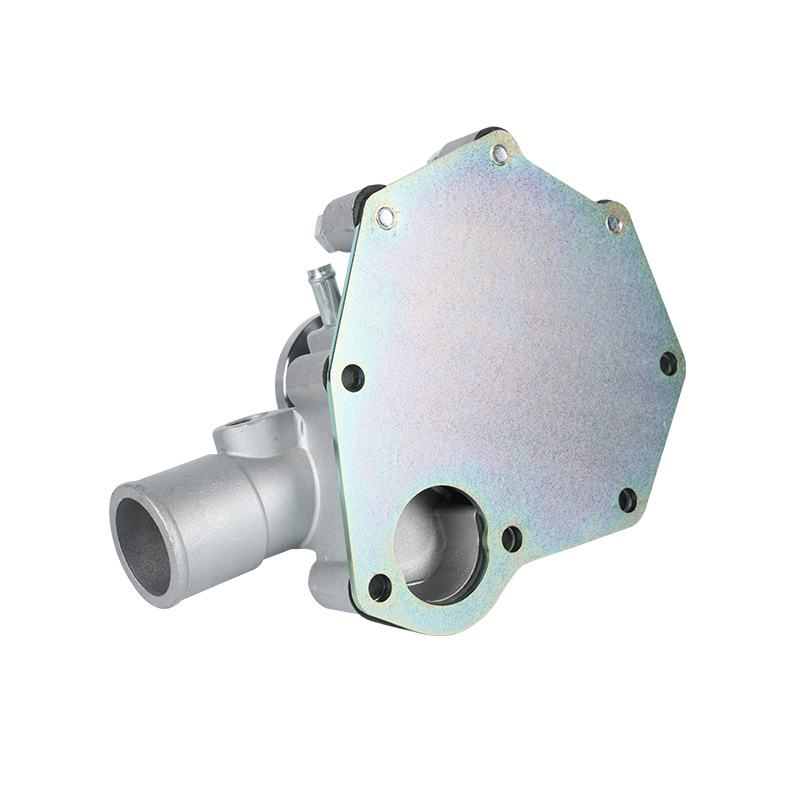
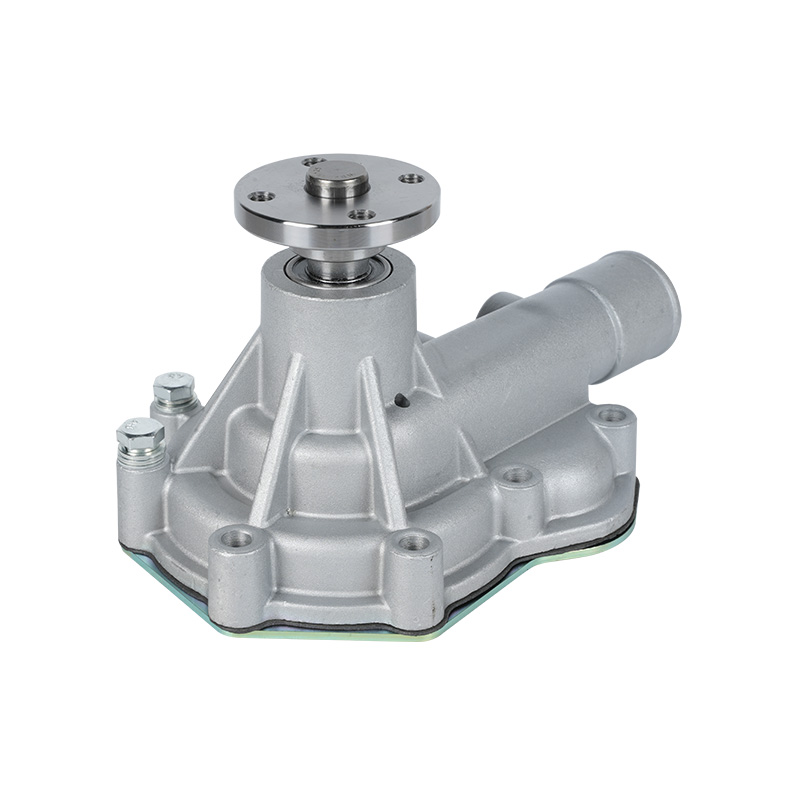
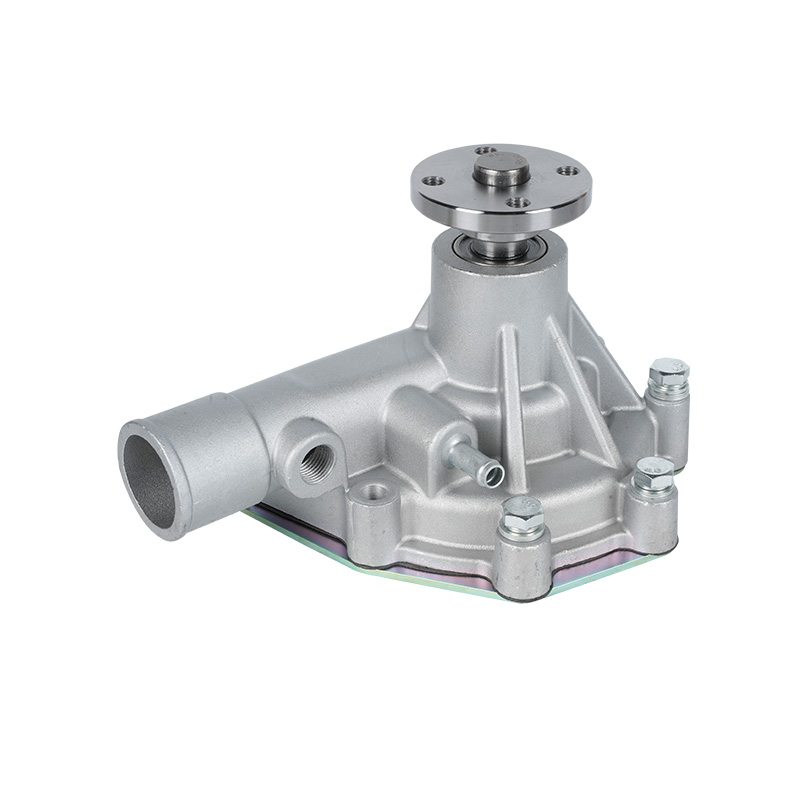
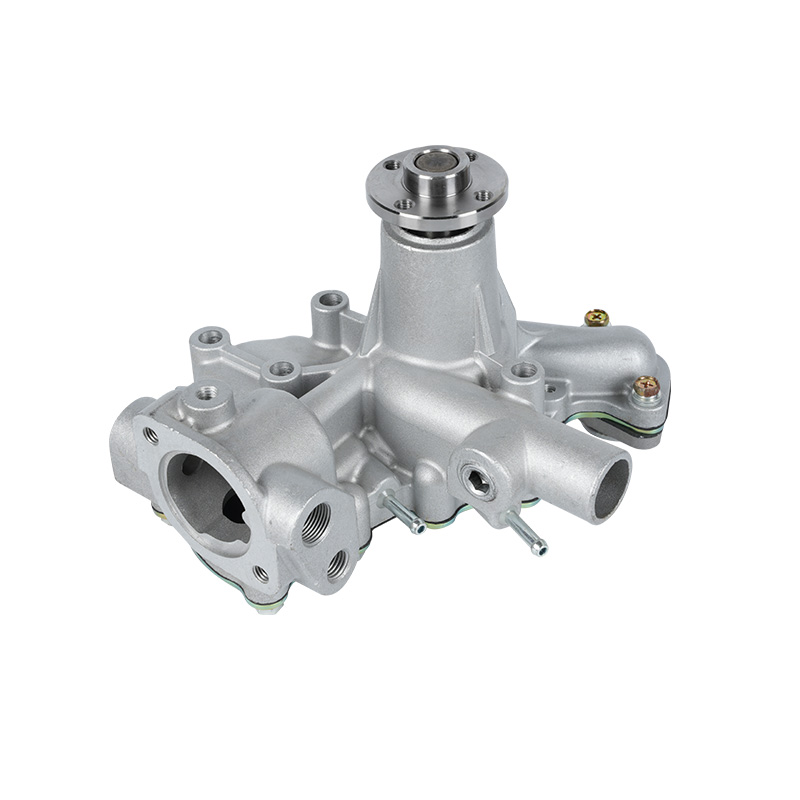
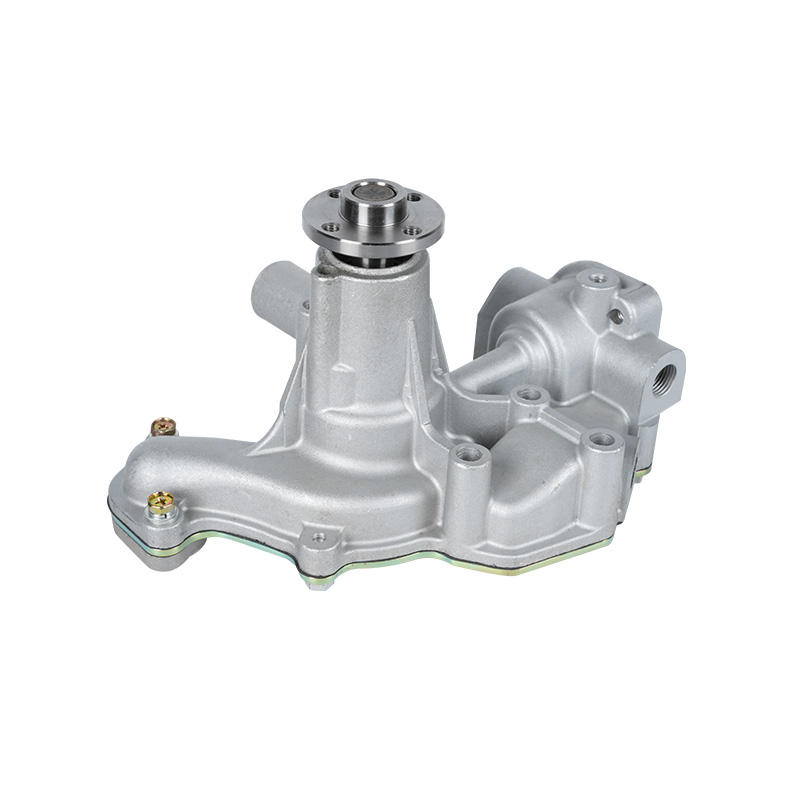
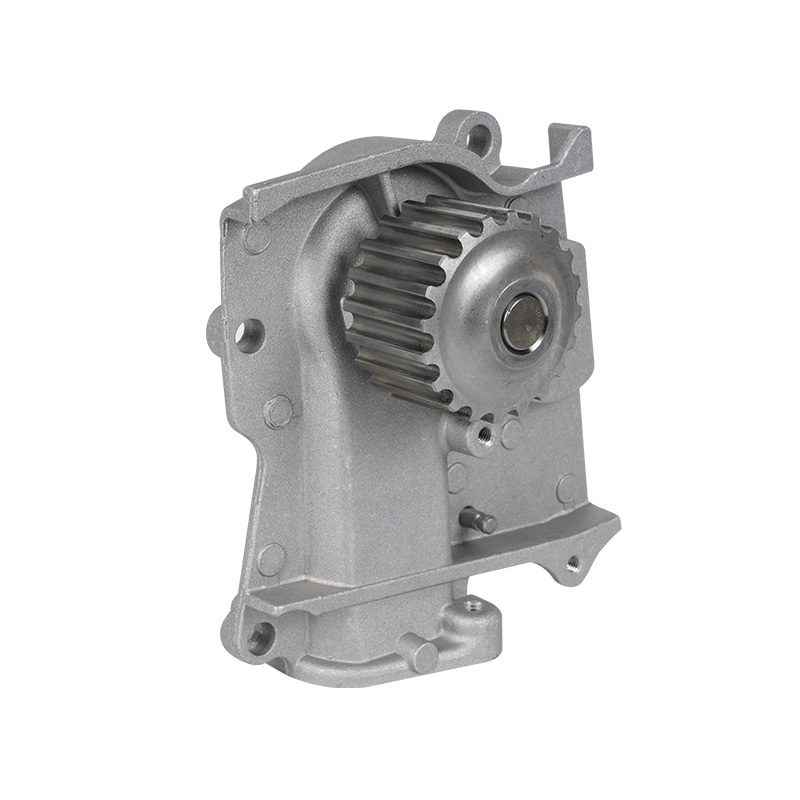
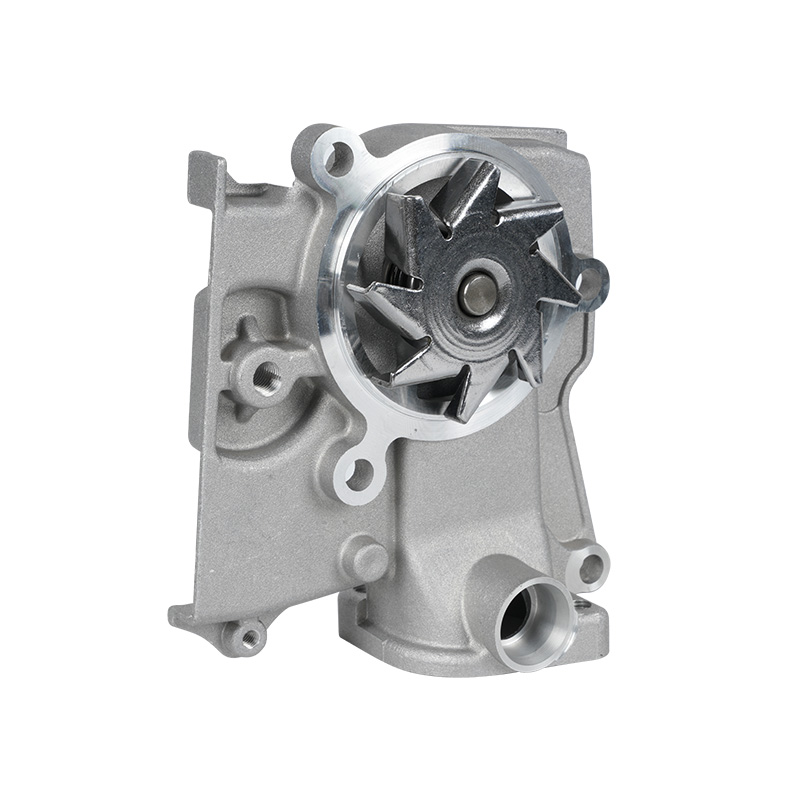
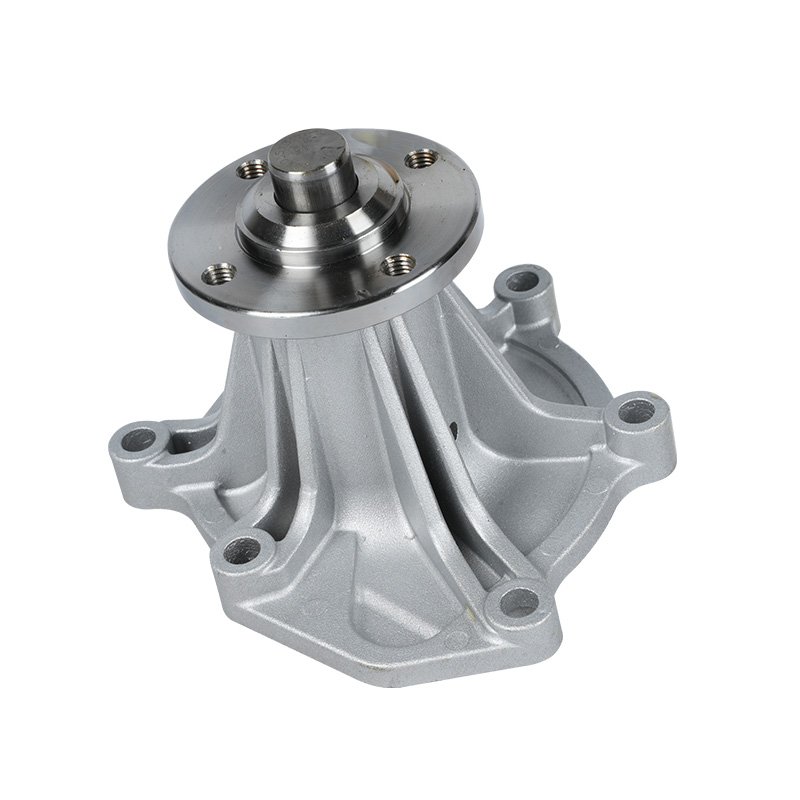
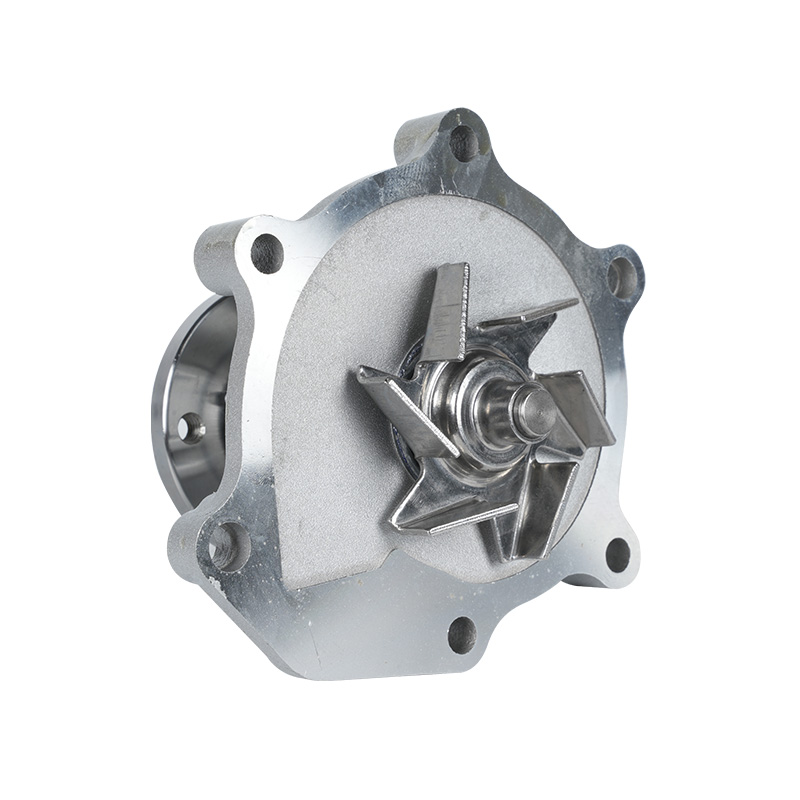
The fundamental and non-negotiable function of an engine water pump is to maintain a stable engine operating temperature by forcing coolant through the engine block and radiator. An overheated engine can suffer catastrophic damage within minutes, making the reliable circulation provided by the engine water pump absolutely vital. It works on a centrifugal principle, where an impeller spun by the pump shaft draws coolant in from the lower radiator hose and flings it outward into the engine's water jackets. This continuous flow absorbs excess heat from the cylinders and cylinder head, carries it to the radiator for dissipation, and then returns cooled fluid to repeat the cycle. This precise thermal regulation ensures ideal combustion, protects engine components from thermal stress, and allows auxiliary systems like the cabin heater to function.
How Are Engine Water Pumps Driven?
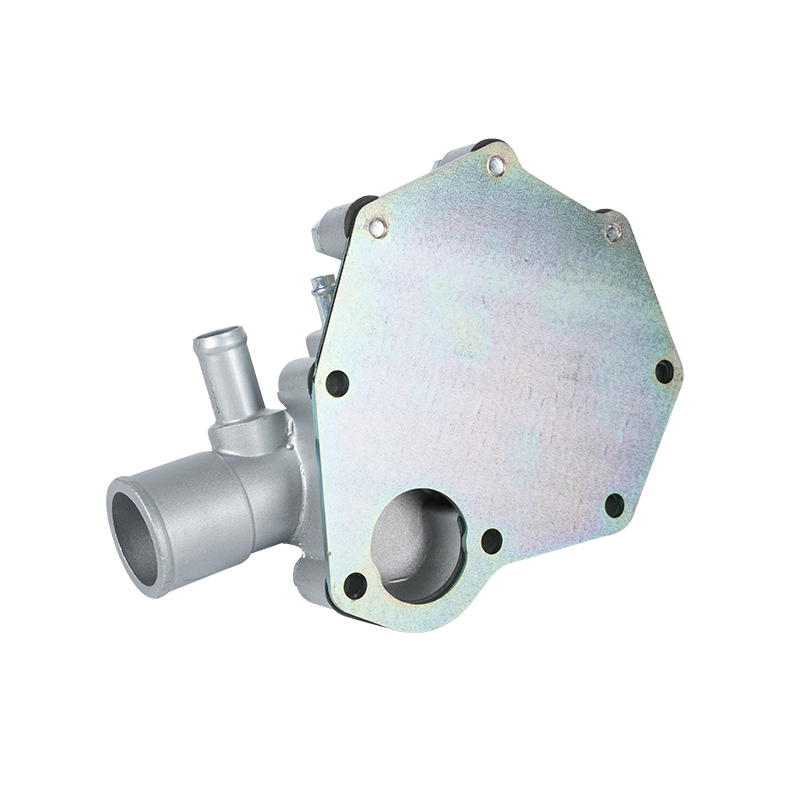
The method of driving the engine water pump has been a primary area of differentiation and innovation. For decades, the dominant method was the mechanical engine water pump, directly powered by the engine itself via a serpentine or timing belt. This simple and robust design means pump speed is directly tied to engine RPM, which can lead to overcooling at high speeds and reduced flow at low speeds. The evolution toward electrification introduced the electric or electronic engine water pump. This type is powered by the vehicle's electrical system and controlled by the Engine Control Unit (ECU). It operates independently of engine speed, allowing for precise, demand-based cooling. This enables features like continued coolant circulation after engine shutdown to prevent heat soak and targeted cooling for specific components like turbochargers. In modern vehicles, it is increasingly common to find multiple engine water pumps—a primary mechanical unit and one or more auxiliary electric pumps—working in concert for complex thermal management.
How is Technology Developing the Future of These Pumps?
Technological development in engine water pumps is tightly focused on enhancing system efficiency, reliability, and integration. Modern mechanical pumps benefit from improved bearing and seal technologies, with some manufacturers extending replacement intervals well beyond 100,000 miles. The rise of the electric engine water pump represents a major development, with its adoption accelerating in both conventional and hybrid vehicles. Its ability to operate only when needed contributes to overall fuel economy improvements. Data suggests that intelligent thermal management systems utilizing smart pumps can contribute to measurable reductions in fuel consumption and emissions by allowing the engine to reach ideal temperature faster and maintain it more consistently. Looking forward, the role of the engine water pump is expanding into battery and power electronics cooling in electric vehicles, where precise temperature control is even more critical for range, performance, and battery longevity. The integration of sensors for real-time flow and temperature monitoring is also paving the way for predictive maintenance, alerting to potential issues before they lead to failure.
The engine water pump has evolved from a passive, engine-driven device into an active, intelligent component central to vehicle thermal strategy. Its core function of heat management remains unchanged, but the methods of achieving it are becoming more sophisticated, efficient, and crucial for meeting the stringent performance and environmental standards of modern and future mobility.
The CXL-E-011 from ZHEJIANG JINRUI PUMP INDUSTRY CO., LTD. is engineered as a high-pressure multi-stage centrifugal pump for demanding industrial and commercial fluid transfer. Its design features a series of precision impellers within a vertically segmented casing to efficiently generate substantial discharge pressure. This makes it highly suitable for critical applications including boiler feed water systems, industrial process water supply, high-pressure cleaning, and reverse osmosis (RO) pure water support. Built with robust materials such as stainless steel for key components, the pump ensures long service life, reliable operation under continuous duty, and efficient performance in systems where maintaining stable, elevated pressure is essential.



 English
English 中文简体
中文简体